Unlocking the Potential — Chapter 1:
A Deep Dive into Bifrost App Chain Liquid Staking Strategy

On April 13, 2023, Ethereum smoothly activated the Shanghai upgrade and opened the staking withdrawal feature, clearing the last hurdle for the thriving narrative of Liquid Staking and Liquid Staking Tokens (LST). Over the past year, whether it’s the rapid increase in TVL (Total Value Locked) of LST protocols or the newfound prosperity of Liquid Staking Finance (LSTFi) with restaking and its liquid re-staked tokens (LRT), it seems to foreshadow a resurgence reminiscent of the DeFi Summer of 2021. Looking back on the crypto industry in 2024, many may refer to it as the “Year of Staking.”
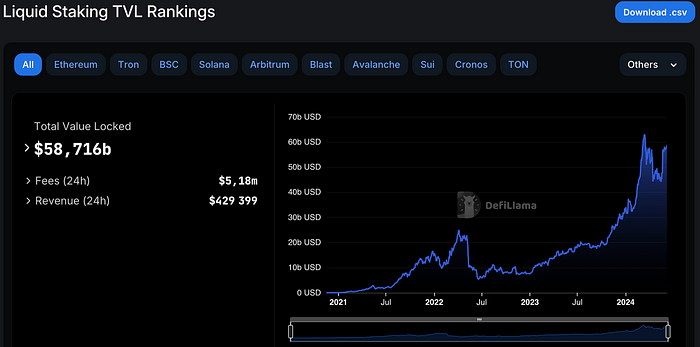
However, the industry’s attention seems to be predominantly focused on LST protocols on Ethereum, with little attention paid to LST on other chains. This is not surprising, given Ethereum’s market capitalization and the far-reaching prosperity of DeFi, which far surpasses that of other new public chains, providing more possibilities for developing and evolving LST protocols and innovative money legos that can be built on top of this primitive.

If we broaden our view to include a wider range of PoS public chains, we will discover that some significant innovations bring fresh insights to the LST industry. Today, we want to introduce a LST protocol that originated from Polkadot.
Bifrost is a dedicated modular Liquid Staking L1 secured by Polkadot and built with the Polkadot SDK. Over the past six months, Bifrost’s TVL has grown fourfold, firmly establishing its position as the leading LST project within the Polkadot ecosystem.
Bifrost has made many notable innovations in the LST space, and its use of dedicative cross-chain architecture may provide significant competitive advantages in the future omni-chain landscape. Meanwhile, Bifrost continues to expand its support for more chains, providing liquid staking services to its ecosystem and beyond.
This article will provide a detailed introduction to Bifrost, offering insights into the architecture of Bifrost — Core advantages of the SLP protocol, SLPx protocol, and its LSTs “vTokens.”
Staking Liquidity Protocol (SLP) and vToken
vToken is an LST asset created by Bifrost, short for Voucher Token. Bifrost currently supports 9 chains and has launched 9 types of vTokens, as shown in the image below:
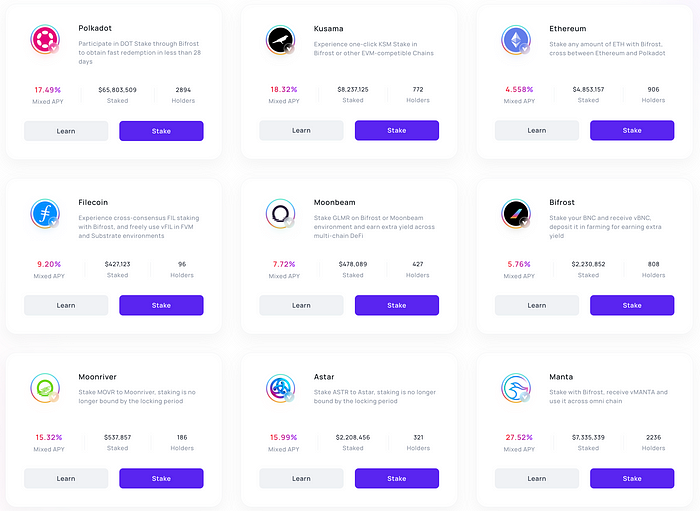
Among them, vDOT, vKSM, vGLMR, vMOVR, vBNC, and vASTAR are all LST assets in the Polkadot ecosystem, with Bifrost’s vToken enjoying an absolute dominant market share in the Polkadot ecosystem.
The module used by Bifrost to support vTokens is known as Staking Liquidity Provider (SLP). Bifrost has deployed the SLP module on Ethereum, Bifrost Polkadot, and Bifrost Kusama. The SLP module manifests as smart contracts on Ethereum to support the minting of vETH, while on Bifrost Polkadot and Bifrost Kusama, it takes the form of a runtime. Bifrost Kusama is the parachain of Polkadot’s pioneer network, Kusama, supporting the minting of vKSM, vBNC, and vMOVR. On the other hand, Bifrost Polkadot functions as the parachain of Polkadot, facilitating the minting of vDOT, vGLMR, vASTR, vFIL, and vMANTA.
As cross-chain bridge infrastructure matures, Bifrost will consolidate all vToken minting and management on the Bifrost Polkadot parachain in the future.
The operation of the SLP module is straightforward: users deposit the original tokens into accounts managed by the SLP module. The SLP module then creates voucher/receipt certificates, or vTokens, for users and stakes the original tokens to the network.
SLPx is an extension module developed based on SLP, serving as a developer toolkit that enables the minting of vTokens on any chain. We aim to make it easier for more DeFi applications to integrate vTokens. For developers of DeFi applications on any chain, integrating SLPx requires only a few simple lines of code. After integration, developers can use remote calls to access the minting, redemption, and exchange services of vTokens on the Bifrost Polkadot chain..
Redemption of vTokens

Typically, when a user initiates the redemption of vTokens, the SLP module needs to request the corresponding amount of original tokens for unstaking and, after the unbonding period ends, return these original tokens to the user.
Unlike the unlock waiting periods of PoS chains, such as 28 days for Polkadot and 7 days for Kusama, Ethereum does not have a fixed unlock waiting period; it depends on the amount of ETH waiting to be unlocked in the queue. The unlock waiting period is a protective measure implemented by PoS chains to prevent long-range attacks.
Like most LST protocols, Bifrost’s vTokens support users in achieving quick redemption through swapping. Bifrost provides a Stable Pool for vToken/Token pairs, adopting a Stable curve similar to Curve Finance to reduce the price impact caused by exchanging.
However, swapping inevitably results in slippage. Bifrost also offers another option for quick redemption. When a user initiates redemption, Bifrost first matches with minting orders in the current queue on a peer-to-peer basis. If the match is successful, the user’s redemption will bypass the unlock waiting period and be cashed out immediately.
The Yield of vToken
Although Bifrost charges a 10% commission from the staking yield of vTokens, the yield of vTokens is often higher than that of competitors. This is because the yield of vTokens is diversified. In addition to the basic staking yield, Bifrost also shares the MEV (Miner Extractable Value) earnings of nodes with users. Periodic mint drop events enable vToken holders to receive BNC rewards.
As a neutral protocol layer, Bifrost ensures that users receive all other rights from the original tokens. For example, vDOT users enjoy the same governance rights in OpenGov as those holding DOT, as well as entitlements from PINK and VARCH airdrops. Bifrost strives to minimize any opportunity costs for vToken holders.

Moreover, Bifrost aims to enrich the use cases of vTokens, allowing users to access more diverse earnings and higher compounded yields in DeFi through vTokens. This aspect is crucial, and we will elaborate on it in the following sections.
The Reward Distribution of vToken
Looking at the development history of LST protocols, we observe that the dividend distribution method has evolved through three stages, from manual claiming to Rebasing, and Reward-bearing. Despite being an established LST protocol launched in 2019, Bifrost was among the first to recognize the superiority of Reward-Bearing. While most competitors used the Claim or Rebasing mechanism, Bifrost had already adopted the Reward-bearing mechanism.
The concept of Reward-bearing refers to accumulating staking rewards into the redemption rights of vTokens, thereby causing the exchange rate between vTokens and the original tokens to increase continuously. This approach eliminates the need for a fixed 1:1 exchange ratio between vTokens and the original tokens. Instead, it reflects the accumulation of staking rewards through changes in the exchange rate.

For example, suppose you initially staked 1 DOT and minted 1 vDOT. Due to the accumulation of staking rewards, this 1 vDOT might be redeemable for 1.2 DOT by the end of the period. This is what Reward-Bearing entails.
The greatest advantage of Reward-Bearing is that it enables DeFi protocols to better handle and integrate vTokens, allowing their application utilization.
If you wish to delve deeper into this concept, please refer to Bifrost’s research on LST dividend distribution methods.
This is the first article in our series of articles. Look out for our next article, which analyses the current LST market.
